Chapter 8
AC Power
m8.3 Complex Power
The circuit shown in Figure m8.3 operates in sinusoidal steady state at 1000 Hz.
The voltage source amplitude is 2.5 V. Component values are: R = 100 Ω,
C = 1.0 μF, and L = 3.3 mH.
- Find the complex power in rectangular format for each of the four
circuit elements: SSRC, SR, SL, and SC.
- Demonstrate conservation of complex power with these four values.
NI Multisim Measurements
Enter the circuit of Figure m8.3 with an AC_VOLTAGE source. Set the “AC
Analysis Magnitude” parameter to match the amplitude specified in the problem
statement.
- Run a Simulate → Analyses → Single Frequency AC Analysis to
determine the complex powers SSRC, SR, SL, and SC in rectangular
format.
- Demonstrate conservation of complex power with these four values.
Additional helpful tips:
- The single-frequency AC analysis calls element power “P” (which
suggests average power only) but in fact calculates complex power
“S.”
NI Multisim video tutorials:
NI myDAQ Measurements
Build the circuit of Figure m8.3. Activate the circuit with the NI ELVISmx
Function Generator on AO0, and place an op amp voltage follower between
AO0 and the remaining circuit; the voltage follower is necessary to boost the
current drive of the analog output beyond its limit of 2 mA.
Use the NI ELVISmx Oscilloscope to display the device voltage on AI0.
Display the voltage across resistor R on AI1, and realize that this voltage is
proportional to the current through every device in the circuit.
- Measure the complex power for each of the four circuit elements using the
following procedure:
- Read the RMS voltage V rms from the oscilloscope numerical
display,
- Read the RMS current Irms from the oscilloscope numerical
display (divide the measured voltage by the resistance R),
- Measure the time shift between the voltage and current
sinusoids with the oscilloscope cursors,
- Convert time shift to phase angle ϕZ = ϕv -ϕi (see Appendix F
for details),
- Note whether the current waveform lags or leads the voltage; ϕZ
is positive when current lags and negative when current leads,
- Express complex power as S = V rmsIrms
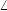 ϕZ, and
ϕZ, and
- Convert S to rectangular form.
- Demonstrate conservation of complex power with these four values.
Additional helpful tips:
- Observe passive sign convention for each circuit element when
measuring voltage and current: positive current enters the positive
polarity terminal.
- Refer to Figure F.1 in Appendix F
to learn how to measure amplitude and phase of a
sinusoidal waveform.
NI myDAQ video tutorials: